Managing Thalassemia in Daily Life
May 30, 2024
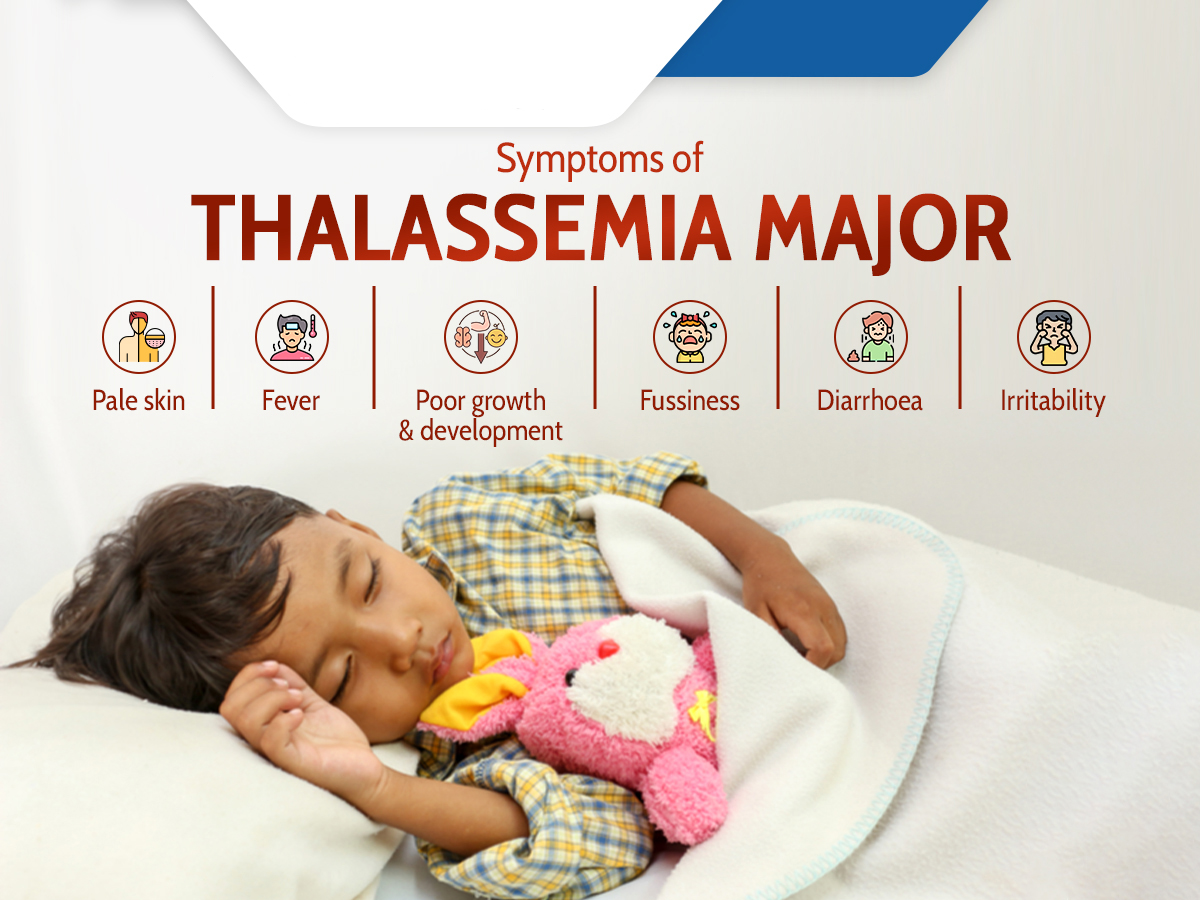
Living with Thalassemia requires a proactive approach to health and well-being. Proper management can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals affected by this condition. Here are some essential strategies to effectively manage Thalassemia in daily life:
1. Regular Medical Check-ups
Consistent visits to healthcare providers are crucial. Regular check-ups help monitor hemoglobin levels, iron levels, and overall health. Early detection of complications allows for timely interventions, preventing severe health issues.
2. Adhering to Treatment Plans
Following prescribed treatment regimens, including regular blood transfusions and iron chelation therapy, is vital. Adherence ensures that hemoglobin levels remain stable and prevents iron overload, which can damage vital organs like the liver and heart.
3. Balanced Nutrition
A well-balanced diet supports overall health and complements medical treatments. Incorporate the following dietary practices:
- High-Quality Protein: Essential for red blood cell production. Include lean meats, fish, eggs, and legumes.
- Folate-Rich Foods: Supports the formation of healthy red blood cells. Include leafy greens, citrus fruits, and fortified cereals.
- Iron Management: Limit iron-rich foods if undergoing iron chelation therapy. Avoid excessive intake of red meat and iron-fortified products unless advised by a healthcare provider.
- Calcium and Vitamin D: Important for bone health, especially if bone deformities are present. Include dairy products, fortified plant-based milks, and sunlight exposure.
4. Physical Activity
Engaging in regular, moderate exercise can enhance physical strength, improve mood, and promote overall well-being. Activities such as walking, swimming, and yoga are beneficial. However, it's important to consult with healthcare providers before starting any new exercise regimen to ensure it aligns with individual health conditions.
5. Emotional and Psychological Support
Managing a chronic condition like Thalassemia can be emotionally challenging. Seeking support through counseling, support groups, or therapy can help individuals and their families cope with stress, anxiety, and other emotional burdens.
6. Education and Awareness
Understanding Thalassemia empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health. Attend educational seminars, read credible sources, and stay updated with the latest research and treatment advancements.
7. Preventing Infections
Individuals with Thalassemia, especially those undergoing regular transfusions, are at a higher risk of infections. Adhere to hygiene practices, get vaccinated as recommended, and avoid exposure to contagious illnesses to minimize infection risks.
8. Bone Health Management
Thalassemia can lead to bone marrow expansion and bone deformities. To maintain bone health:
- Ensure adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D.
- Engage in weight-bearing exercises.
- Consult with healthcare providers about potential treatments to prevent bone complications.
9. Genetic Counseling
For individuals planning to start a family, genetic counseling is recommended to understand the risks of passing Thalassemia to offspring. This helps in making informed reproductive choices and exploring options like genetic testing and assisted reproductive technologies.
Conclusion
Managing Thalassemia effectively involves a combination of medical treatment, lifestyle adjustments, and emotional support. By adhering to treatment plans, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and seeking support when needed, individuals with Thalassemia can lead fulfilling and active lives. Continuous collaboration with healthcare providers and staying informed about the condition are key components of successful management.